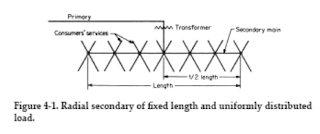
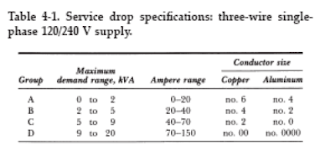
Transformers play a central part in the design of distribution systems;
they reduce the high voltage of the primary to the low utilization
voltage of the secondary. As with other elements of the distribution circuit,
the energy losses and the drop in voltage due to the current flowing
through them to supply loads are factors in the selection of the size and
location of transformers.
Losses
Energy losses in a transformer are generally of two kinds:
1. No-load loss (also known as iron or core loss) results from the mag
netizing or exciting current flowing in the primary coil regardless
of the load carried. Its value of about 0.5 percent at rated full load
may vary substantially at voltages above or below rated values.
Although small as a power loss, it goes on constantly, accumulating
into significant annual energy losses (in kilo-watt-hours).
2. Full-load losses (earlier known as copper losses) result from the
load current passing through the resistance of both primary and
secondary coils. This I^R loss varies with the square of the current
carried and therefore depends on the shape of the load curve. Since
the current flowing in a circuit is inversely proportional to the
voltage, the copper loss is inversely proportional to the square of
the voltage; hence, for the same-size transformer, the losses in the
primary coil are substantially less as the voltage ratings increase.
No-load and full-load losses for the various sizes of transformers vary
with different manufacturers and are usually specified by them in some
percentage of normal voltage and full-load ratings. No-load losses may be
expressed in watts or as a percentage of the full rated load in watts.
Impedance—Resistance and Reactance
Copper losses, as well as voltage regulation, require that resistance
and reactance values (and their vector sum, impedance) of the
transformer be known. These three values represent both primary and
secondary coils of the transformer. They are usually specified by the
manufacturer as a percentage related to the percentage voltage drop.
That percentage gives a value in volts when applied to either primary
or secondary voltage; from that voltage and the full rated current the
values in ohms may be derived.
The percentage impedance given for a transformer represents (and
is equivalent to) the percentage drop from normal rated primary voltage
that would occur when full rated load current flows in the secondary;
thus the percentage impedance can be used to determine the impedances
(in ohms) of the primary and secondary as follows.
Voltage Drop
The determination of voltage drop through the transformer employs
values of impedance, resistance, and reactance, as indicated in the
previous discussion of primary and secondary systems. The drop must
be referred to either the primary or the secondary side:
Voltage drop (primary) = Ip(Rp cos θ + X sin θ)
where Ip is the load current and cos θ the power factor.
Voltage drop (secondary) = Is(Rs cos θ + X sin θ)
% voltage drop voltage drop (primary) voltage drop (secondary)
——————— = —————————— = ———————————
100 rated primary voltage rated secondary voltage
These same phase-to-neutral values of Z, R, and X can also be employed
in polyphase circuits. Since phase to phase voltage (for a threephase
circuit) is √3 times the phase-to-neutral value and the voltage
value in the equation is squared, the ratio between phase-to-phase and
phase-to-neutral characteristics is 3 to 1. If the transformer kVA value is
the three-phase total kVA and Ep is the phase-to-phase voltage,
Single-phase
The standard single-phase distribution transformer is generally designed
with the secondary coil in two parts, which may be connected in
parallel for two-wire 120-V operation, or in series for three-wire 120/240
V operation. The latter is the most commonly used connection for singlephase
distribution systems. The load is balanced between two 120-V
circuits; with perfect balance, no current flows in the center or neutral
wire. Refer to Figure 4-6a.
Three-phase
For three-phase systems, the wye-connected secondary can serve
single-phase loads at 120 V for each phase; when the load is balanced,
the neutral will carry no current. This connection can also supply threephase
power loads at 208 V between phases, and it is best adapted for
use on secondary networks. It does have the disadvantage of a lowered
three-phase (208 V) voltage supply to three-phase motors with standard
ratings of 240 V; the 32-V difference, or 13.3 percent, below the rating
may affect the operation of the motors. To remedy the situation, the secondary
voltage is often raised to 125 V, yielding about 217 V between
phases or about only 10 percent less than the standard 240-V rating,
more likely to be within the design tolerances for satisfactory operation.
See Figure 4-6b and c.
The primary supply to this four-wire wye secondary connection
can be either delta- or wye-connected; in the latter case, the wye is usually
grounded to prevent voltage unbalances from unbalanced secondary
loads from distorting phase relationships. Often, further economy is
achieved if both the primary and secondary circuits employ a common
neutral conductor.
Small amounts of three-phase power loads may be supplied on a
chiefly single-phase system by a small-diameter-conductor extension of
another phase and the installation of a small-capacity single-phase transformer
in an open-wye or open-delta bank (on the primary side) with
the principal single-phase transformer.
The secondary of this second
single-phase transformer is connected in an open-delta configuration
with the secondary of the principal transformer, providing a small threephase
delta power supply to the small three-phase requirement. Because
of the phase relationship of the voltage and current, however, only 86
percent of the capacity of this second, small single-phase transformer
can be utilized. This is an economical method of supplying a small,
isolated three-phase load in the midst of an area supplied from singlephase
facilities.
Two-phase
Although two-phase systems are virtually extinct, there are still
some two-phase power loads in existence. These may be supplied from
three-phase delta or wye systems through proper connections of two
single-phase transformers.
Boost-Buck
Earlier, reference was made to the use of single-phase transformers
to boost or buck the line voltage of a primary feeder. Here, the primary
and secondary of the transformer are connected in series, essentially operating
as an autotransformer. The incoming primary coil is connected
across the primary circuit, while the outgoing primary is connected
between a common terminal of the primary of the transformer and the
terminal of the secondary coil; the voltage of the secondary coil is either
added to boost the primary voltage or subtracted to buck it. The capacity
of the secondary coil limits the primary current that may flow through
it.
Three-phase Units
Connections for three-phase transformers and lead markings are
shown in the IEEE classification of polarities.
Autotransformers
Under certain conditions, when the ratio of transformation desired
is low, usually not greater than about 5 to 1, and electrical isolation
between primary and secondary circuits is not essential, the autotransformer
has some advantages.
The autotransformer consists of one winding, a part of which may
serve as both primary and secondary. In a two-winding transformer, all
of the energy is transformed by magnetic action. In the autotransformer,
a portion only is transformed magnetically and the remainder flows
conductively through a part of its windings. Since only a portion of the
energy is transferred, the autotransformer can be smaller than a twowinding
unit; comparable costs of the unit and its installation are less.
Read More - Transformers
they reduce the high voltage of the primary to the low utilization
voltage of the secondary. As with other elements of the distribution circuit,
the energy losses and the drop in voltage due to the current flowing
through them to supply loads are factors in the selection of the size and
location of transformers.
Losses
Energy losses in a transformer are generally of two kinds:
1. No-load loss (also known as iron or core loss) results from the mag
netizing or exciting current flowing in the primary coil regardless
of the load carried. Its value of about 0.5 percent at rated full load
may vary substantially at voltages above or below rated values.
Although small as a power loss, it goes on constantly, accumulating
into significant annual energy losses (in kilo-watt-hours).
2. Full-load losses (earlier known as copper losses) result from the
load current passing through the resistance of both primary and
secondary coils. This I^R loss varies with the square of the current
carried and therefore depends on the shape of the load curve. Since
the current flowing in a circuit is inversely proportional to the
voltage, the copper loss is inversely proportional to the square of
the voltage; hence, for the same-size transformer, the losses in the
primary coil are substantially less as the voltage ratings increase.
No-load and full-load losses for the various sizes of transformers vary
with different manufacturers and are usually specified by them in some
percentage of normal voltage and full-load ratings. No-load losses may be
expressed in watts or as a percentage of the full rated load in watts.
Impedance—Resistance and Reactance
Copper losses, as well as voltage regulation, require that resistance
and reactance values (and their vector sum, impedance) of the
transformer be known. These three values represent both primary and
secondary coils of the transformer. They are usually specified by the
manufacturer as a percentage related to the percentage voltage drop.
That percentage gives a value in volts when applied to either primary
or secondary voltage; from that voltage and the full rated current the
values in ohms may be derived.
The percentage impedance given for a transformer represents (and
is equivalent to) the percentage drop from normal rated primary voltage
that would occur when full rated load current flows in the secondary;
thus the percentage impedance can be used to determine the impedances
(in ohms) of the primary and secondary as follows.
Voltage Drop
The determination of voltage drop through the transformer employs
values of impedance, resistance, and reactance, as indicated in the
previous discussion of primary and secondary systems. The drop must
be referred to either the primary or the secondary side:
Voltage drop (primary) = Ip(Rp cos θ + X sin θ)
where Ip is the load current and cos θ the power factor.
Voltage drop (secondary) = Is(Rs cos θ + X sin θ)
% voltage drop voltage drop (primary) voltage drop (secondary)
——————— = —————————— = ———————————
100 rated primary voltage rated secondary voltage
These same phase-to-neutral values of Z, R, and X can also be employed
in polyphase circuits. Since phase to phase voltage (for a threephase
circuit) is √3 times the phase-to-neutral value and the voltage
value in the equation is squared, the ratio between phase-to-phase and
phase-to-neutral characteristics is 3 to 1. If the transformer kVA value is
the three-phase total kVA and Ep is the phase-to-phase voltage,
Single-phase
The standard single-phase distribution transformer is generally designed
with the secondary coil in two parts, which may be connected in
parallel for two-wire 120-V operation, or in series for three-wire 120/240
V operation. The latter is the most commonly used connection for singlephase
distribution systems. The load is balanced between two 120-V
circuits; with perfect balance, no current flows in the center or neutral
wire. Refer to Figure 4-6a.
Three-phase
For three-phase systems, the wye-connected secondary can serve
single-phase loads at 120 V for each phase; when the load is balanced,
the neutral will carry no current. This connection can also supply threephase
power loads at 208 V between phases, and it is best adapted for
use on secondary networks. It does have the disadvantage of a lowered
three-phase (208 V) voltage supply to three-phase motors with standard
ratings of 240 V; the 32-V difference, or 13.3 percent, below the rating
may affect the operation of the motors. To remedy the situation, the secondary
voltage is often raised to 125 V, yielding about 217 V between
phases or about only 10 percent less than the standard 240-V rating,
more likely to be within the design tolerances for satisfactory operation.
See Figure 4-6b and c.
The primary supply to this four-wire wye secondary connection
can be either delta- or wye-connected; in the latter case, the wye is usually
grounded to prevent voltage unbalances from unbalanced secondary
loads from distorting phase relationships. Often, further economy is
achieved if both the primary and secondary circuits employ a common
neutral conductor.
Small amounts of three-phase power loads may be supplied on a
chiefly single-phase system by a small-diameter-conductor extension of
another phase and the installation of a small-capacity single-phase transformer
in an open-wye or open-delta bank (on the primary side) with
the principal single-phase transformer.
The secondary of this second
single-phase transformer is connected in an open-delta configuration
with the secondary of the principal transformer, providing a small threephase
delta power supply to the small three-phase requirement. Because
of the phase relationship of the voltage and current, however, only 86
percent of the capacity of this second, small single-phase transformer
can be utilized. This is an economical method of supplying a small,
isolated three-phase load in the midst of an area supplied from singlephase
facilities.
Two-phase
Although two-phase systems are virtually extinct, there are still
some two-phase power loads in existence. These may be supplied from
three-phase delta or wye systems through proper connections of two
single-phase transformers.
Boost-Buck
Earlier, reference was made to the use of single-phase transformers
to boost or buck the line voltage of a primary feeder. Here, the primary
and secondary of the transformer are connected in series, essentially operating
as an autotransformer. The incoming primary coil is connected
across the primary circuit, while the outgoing primary is connected
between a common terminal of the primary of the transformer and the
terminal of the secondary coil; the voltage of the secondary coil is either
added to boost the primary voltage or subtracted to buck it. The capacity
of the secondary coil limits the primary current that may flow through
it.
Three-phase Units
Connections for three-phase transformers and lead markings are
shown in the IEEE classification of polarities.
Autotransformers
Under certain conditions, when the ratio of transformation desired
is low, usually not greater than about 5 to 1, and electrical isolation
between primary and secondary circuits is not essential, the autotransformer
has some advantages.
The autotransformer consists of one winding, a part of which may
serve as both primary and secondary. In a two-winding transformer, all
of the energy is transformed by magnetic action. In the autotransformer,
a portion only is transformed magnetically and the remainder flows
conductively through a part of its windings. Since only a portion of the
energy is transferred, the autotransformer can be smaller than a twowinding
unit; comparable costs of the unit and its installation are less.